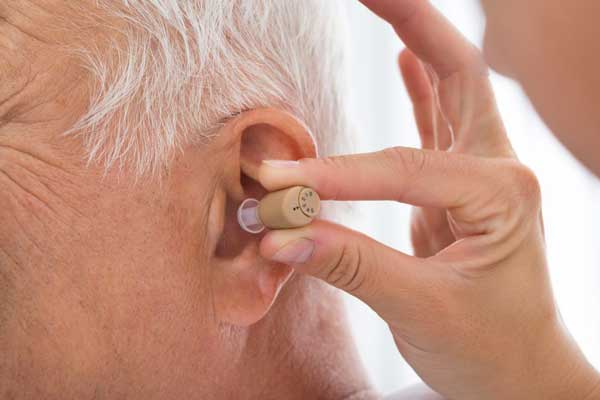
Hearing Aids
Hearing aids are small electronic devices worn in or behind the ear that help people with hearing loss hear more clearly. They work by amplifying sound, making it easier to hear speech and environmental sounds.
Who Needs Hearing Aids
- People with sensorineural hearing loss (due to damage in the inner ear or auditory nerve).
- Hearing aids don’t restore normal hearing, but they improve hearing ability, especially in:
- Conversations
- Noisy environments
- Watching TV or listening to mu
What you need to know
Types Of Hearing Aids
We offer all
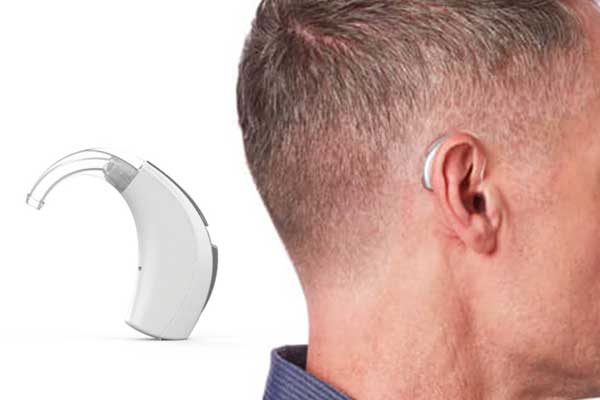
Behind-the-Ear (BTE)
- Worn behind the ear with a tube that connects to an ear mold or dome inside the ear.
- Suitable for mild to profound hearing loss.
- Durable and easier to handle.
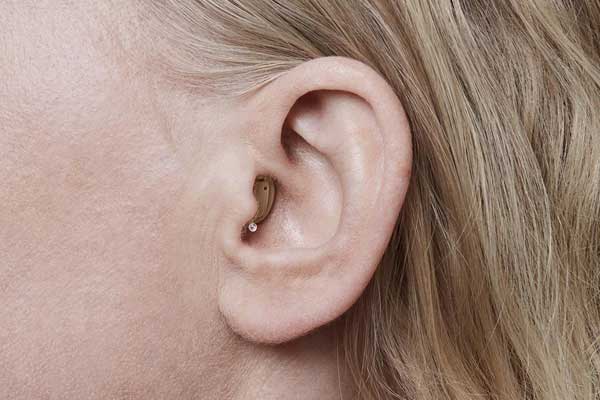
In-the-Canal (ITC) / Completely-in-the-Canal (CIC)
- Small and fit partly or entirely inside the ear canal.
- Very discreet but may be harder to handle.
- Best for mild to moderate hearing loss.
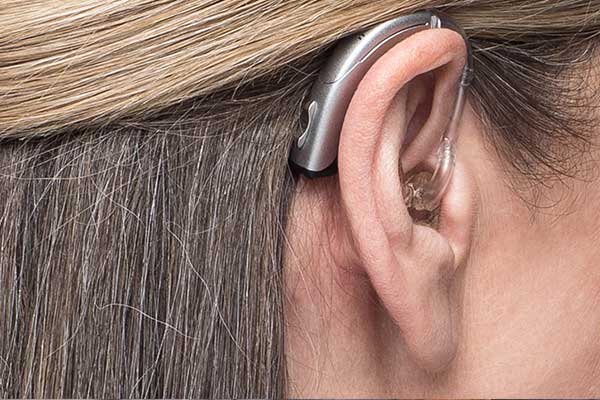
Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) or Receiver-in-the-Ear (RITE)
- Similar to BTE but smaller and more discreet.
- The speaker sits inside the ear canal, connected by a thin wire.
- Popular for mild to severe loss.
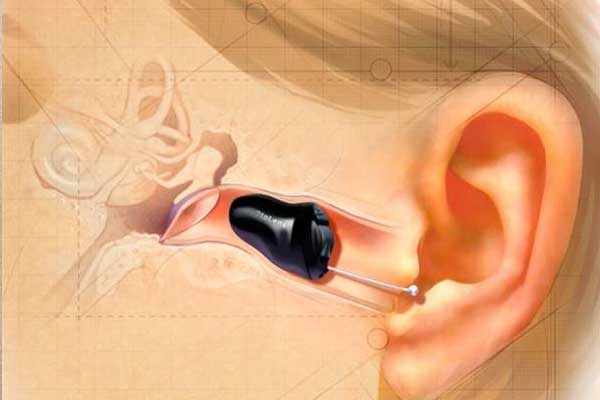
Invisible-in-the-Canal (IIC)
- Deeply inserted into the ear canal.
- Virtually invisible.
- Used for mild to moderate hearing loss.
Features of Modern Hearing Aids
- Noise reduction
- Directional microphones (focus on sounds in front of you)
- Bluetooth connectivity (stream from phones, TVs, etc.)
- Rechargeable batteries
- Feedback cancellation (reduce whistling)
- Telecoil (for use with hearing loop systems)
Remote control via smartphone apps
Things to Know
- You need a hearing test by an audiologist to get properly fitted.
- Adaptation takes time – your brain needs to adjust to amplified sounds.
- Hearing aids can last 3–7 years depending on care and type.
- Not all hearing aids are covered by insurance – check local policies or programs.