Hearing Tests
Hearing tests are medical or diagnostic exams that evaluate how well a person can hear sounds. They help determine the type, degree, and sometimes the cause of hearing loss. These tests are usually performed by an audiologist.
What you need to know
Types of Hearing Tests
We Offer All
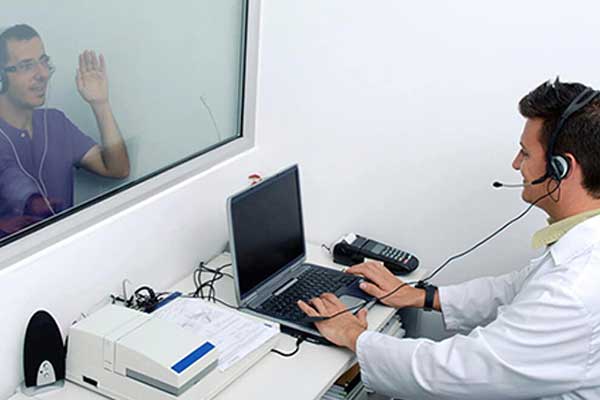
Pure Tone Audiometry (Standard Hearing Test)
- What it does: Measures the softest sounds a person can hear at different pitches (frequencies).
- How it works:
- You wear headphones.
- You listen to tones of various pitches and volumes.
- You raise your hand or press a button when you hear a sound.
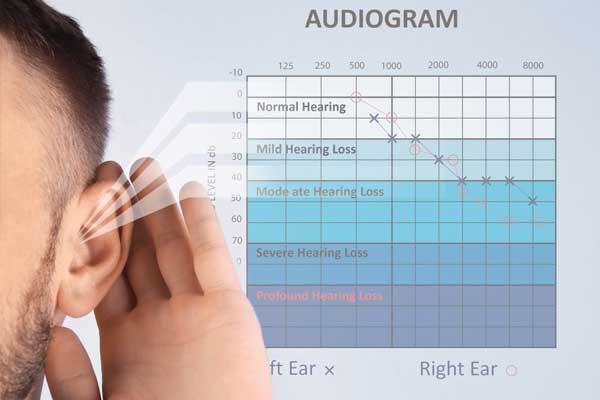
- Results are charted on an audiogram.
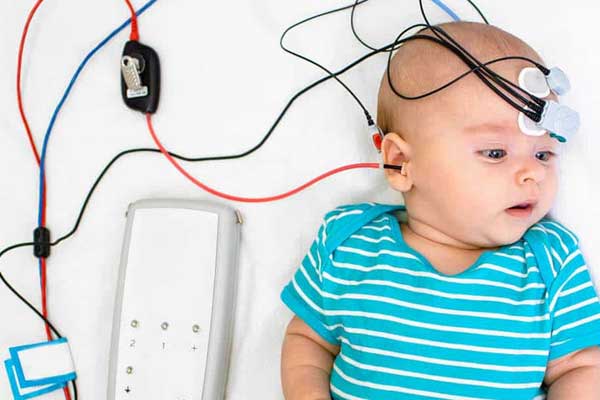
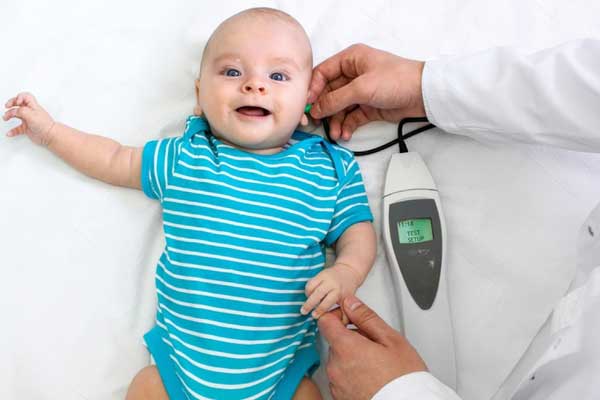
Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR)
- What it does: Checks how well sound travels from the ear to the brainstem.
- Used for: Infants, people who can’t respond to standard tests, or when neurological issues are suspected.
- How it works:
- Electrodes are placed on the scalp.
- Clicks or tones are played, and the brain's response is recorded.
Tympanometry (Middle Ear Test)
- What it does: Checks the movement of the eardrum and middle ear function.
- How it works:
- A small probe is placed in the ear canal.
- Air pressure changes are introduced to measure eardrum movement.
- Can detect fluid, perforations, or Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Interpreting Results
- Hearing is measured in decibels (dB) (loudness) and hertz (Hz) (frequency).
- Results tell whether hearing loss is:
- Normal
- Mild
- Moderate
- Severe
- Profound
The audiogram shows the thresholds at which you start to hear each frequency.
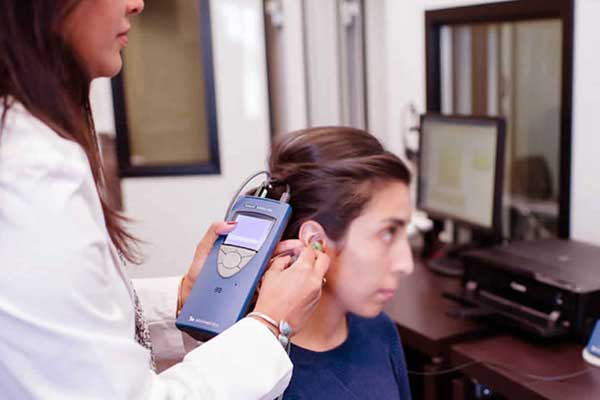
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE)
- What it does: Measures sound waves produced by the inner ear (cochlea).
- Often used in: Newborn hearing screenings.
- How it works:
- A tiny microphone and speaker go in the ear.
- The ear’s response to sounds is measured.
- No response may suggest inner ear damage.
When to Get a Hearing Test
- Trouble understanding conversations
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ears
- Frequent need to turn up the TV
- Family or friends notice changes in your hearing
- As part of routine checkups (especially for children or older adults)